The researchers report in the Journal of Neuroscience that when mice allowed to exercise regularly experienced a stressor — exposure to cold water — their brains exhibited a spike in the activity of neurons that shut off excitement in the ventral hippocampus, a brain region shown to regulate anxiety. These findings potentially resolve a discrepancy.. read more →
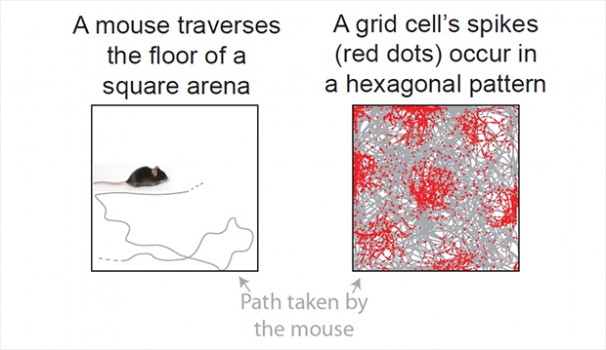
Just as a global positioning system (GPS) helps find your location, the brain has an internal system for helping determine the body’s location as it moves through its surroundings. A new study from researchers at Princeton University provides evidence for how the brain performs this feat. The study, published in the journal Nature, indicates that.. read more →
Using sea snail nerve cells, the scientists reversed memory loss by determining when the cells were primed for learning. The scientists were able to help the cells compensate for memory loss by retraining them through the use of optimized training schedules. Findings of this proof-of-principle study appear in The Journal of Neuroscience. “Although much works.. read more →
Children with dyslexia may read better after playing action video games that stress mayhem, not literacy, a contested study suggests. Playing fast-paced Wii video games for 12 hours over two weeks markedly increased the reading speed of 7- to 13-year-old kids with dyslexia, with no loss of reading accuracy, says a team led by psychologist.. read more →
The results of these projects suggest the future potential for linking multiple brains to form what the research team is calling an “organic computer,” which could allow sharing of motor and sensory information among groups of animals. The study was published Feb. 28, 2013, in the journal Scientific Reports. “Our previous studies with brain-machine interfaces.. read more →
Aug. 15, 2011 — Ultra-thin electronics, which can be placed on the skin as easily as a temporary tattoo, could pave the way for patient monitoring systems that would avoid the need for bulky equipment. In one study, the adhesive patch was applied to a person’s chest to pick up electrical signals produced by the.. read more →
This study sought to investigate the attentional demands while performing a blind navigation task in young and elderly subjects. Fourteen subjects of age 20 to 32 years and 10 subjects of age 62 to 80 years participated in the experience. Blinded navigation task consisted of visually identifying and then walking blindly towards a target 8.. read more →
Researchers at XenoBiotic Laboratories are using cryo-imaging and quantitative autoradiography to provide quantitative tissue distribution data as part of a preclinical ADME program. Autoradioluminograms placed through 3D reconstructed organs are highlighted in this video. read more →
For the first time, researchers decipher the retina’s neural code for brain communication to create novel, more effective prosthetic retinal device for blindness. Two researchers at Weill Cornell Medical College have deciphered a mouse’s retina’s neural code and coupled this information to a novel prosthetic device to restore sight to blind mice. The researchers say.. read more →
Signs of depression can be turned on and off in mice with the flip of a switch. Activating or silencing the behavior of certain brain cells with laser light causes the animals to change their depressive behavior, two new studies find. Although the experiments were done in rodents, the results have direct relevance to human.. read more →
